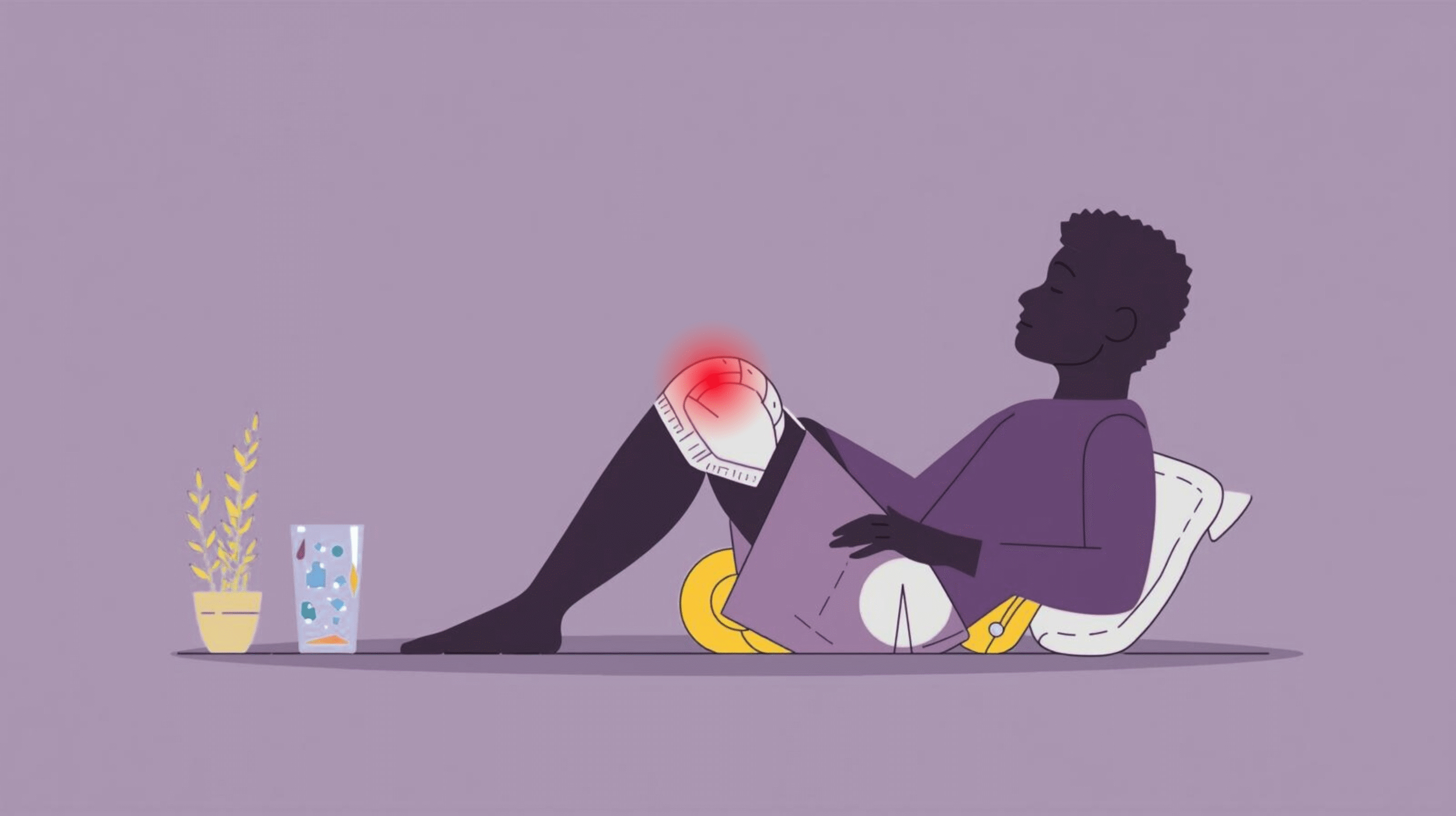
A swollen knee, or knee effusion, is a commonly occurring condition that involves the accumulation of excess fluid in or around the knee joint [1]. This accumulation is responsible for causing pain, stiffness, warmth, redness, and difficulty in moving the knee. Some swelling develops right after the injury. In other cases, it appears gradually due to chronic conditions such as arthritis, gout, or repeated stress on the knee. People with swollen knees struggle to do daily activities and it impacts overall life quality. Understanding how to manage a swollen knee at home is crucial for reducing discomfort, preventing further injury, and maintaining mobility, particularly when immediate medical care may not be accessible.
Managing knee swelling at home involves a combination of rest, natural remedies, diet, gentle exercises, and preventive strategies. It is also important to monitor symptoms carefully and recognize when professional medical intervention is necessary. Minor swelling often responds well to self-care, but persistent or severe cases may indicate an underlying condition requiring diagnosis and treatment.
You can also check related articles:
- https://betterhood.in/learn/knee-joint-pain-causes/
- https://betterhood.in/learn/chronic-knee-pain-due-to-patellar-instability-understanding-the-cause/
How can you understand a swollen knee??
The knee is one of the most complex and vital joints in the body, comprising the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), patella (kneecap), ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Healthy knees contain synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint, reduces friction, and allows smooth movement. Swelling occurs when excess fluid collects due to inflammation, injury, infection, or overuse, stretching the joint capsule and causing stiffness and discomfort.
Knee swelling can be classified into two main types:
- Acute swelling: Appears suddenly after trauma, such as ligament tears, meniscus injuries, or sprains. Symptoms often include immediate pain, redness, and limited mobility.
- Chronic swelling: Develops gradually due to long-term conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or repeated stress. Chronic swelling may fluctuate in intensity and is often associated with persistent stiffness or discomfort.[2]
Recognizing the type of swelling helps determine the appropriate home care measures and whether professional treatment is necessary. Early intervention can prevent worsening of the condition and promote faster recovery.
Common Causes of a Swollen Knee
Understanding the underlying causes of knee swelling is key to effective treatment and prevention. The most common causes include:
1. Injuries:
Ligament injuries, such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL) tears, are a frequent cause of acute swelling. Meniscus tears and minor sprains can also trigger fluid accumulation. Even low-impact injuries can lead to temporary swelling, especially if the joint is overused or stressed.
2. Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage in the knee leads to inflammation and joint fluid buildup.[3][4]
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune condition causing inflammation and swelling of the joint lining.
- Gout: Caused by uric acid crystal deposits in the knee, triggering sudden pain and swelling.
3. Infections:
Bacterial infections such as septic arthritis require immediate medical attention. These infections cause severe swelling, redness, warmth, and often fever. Post-viral inflammation may also lead to temporary swelling that improves with rest and home care.
4. Overuse and repetitive stress:
Activities such as running, jumping, prolonged kneeling, or heavy lifting can irritate the knee joint and lead to fluid retention. This type of swelling is common in athletes or people with physically demanding jobs.
5. Lifestyle factors:
Obesity and sedentary habits increase stress on the knee joint, accelerating wear and tear. Excess weight can also exacerbate swelling in response to minor injuries or chronic conditions.
Symptoms of a Swollen Knee
Knee swelling may manifest in a variety of ways, depending on the underlying cause:
- Pain or tenderness in the joint
- Redness and warmth around the knee
- Stiffness and difficulty bending or straightening the knee
- A feeling of heaviness or pressure inside the joint
- Instability or locking in cases of ligament or meniscus injury
Monitoring these symptoms is crucial. Persistent pain, inability to bear weight, or sudden swelling after trauma should prompt medical evaluation.[5]
Initial Home Care for a Swollen Knee
Immediate care at home can help manage swelling, reduce pain, and prevent further damage. Key steps include:
- Rest: Limiting movement and avoiding high-impact activities prevents aggravating the knee.
- Ice therapy: Applying an ice pack wrapped in a cloth for 15–20 minutes multiple times a day reduces inflammation. Cold therapy is especially effective in the first 24–48 hours after an injury.
- Elevation: Raising the knee above heart level using pillows helps drain excess fluid and minimize swelling.
- Compression: Using a knee sleeve or elastic bandage provides gentle support and reduces fluid accumulation. Avoid wrapping too tightly, which may restrict circulation.
- Monitoring: Keep track of pain levels and swelling. Persistent or worsening symptoms may indicate a more serious problem requiring medical care.
Home Remedies for Swollen Knee
Several natural remedies can complement initial home care to relieve swelling and promote healing:
1. Cold and heat therapy:
- Cold therapy is best for acute swelling, pain relief, and inflammation.
- Heat therapy helps relax muscles, improve blood flow, and relieve stiffness once initial swelling decreases.
2. Gentle massage and mobility exercises:
Light massage around the knee improves circulation, reduces fluid buildup, and encourages recovery. Avoid deep pressure directly on inflamed areas.
3. Herbal remedies and natural supplements:
- Turmeric: Curcumin in turmeric has strong anti-inflammatory properties. Consume as a supplement or in food.
- Ginger and green tea: Contain antioxidants that reduce inflammation.
- Essential oils: Eucalyptus and peppermint oils can provide temporary pain relief when massaged gently on the joint.
4. Dietary support:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, flax seeds, and walnuts, reduce inflammation.
- Calcium and vitamin D-rich foods: Strengthen bones and joints.
- Hydration and low-sodium intake: Prevents fluid retention and promotes joint health.
These remedies, combined with rest and gentle exercises, support faster recovery and reduce the risk of chronic swelling.[6]
Lifestyle Adjustments for Knee Health
Long-term knee health requires consistent lifestyle adjustments:
- Weight management: Reducing excess weight lowers stress on the knee joint.
- Low-impact exercises: Walking, swimming, or cycling improve flexibility without straining the knee.
- Yoga and stretching: Maintain mobility, improve balance, and prevent stiffness.
- Avoiding strain: Limit repetitive high-impact activities like running on hard surfaces or prolonged kneeling.
Incorporating these habits into daily life helps prevent swelling and supports overall joint health.
Exercises to Strengthen and Support the Knee
Strengthening muscles around the knee reduces stress on the joint and helps prevent future swelling. Recommended exercises include:
- Quadriceps strengthening: Straight leg raises and seated knee extensions.
- Hamstring stretches: Improve flexibility and reduce posterior knee strain.
- Balance and stability exercises: Single-leg stands or balance board exercises.
- Guided physiotherapy: Ensures exercises are performed correctly and safely.
Consistent exercise not only alleviates current swelling but also strengthens the joint against future injuries.[7]
When to Seek Medical Attention
While home care can manage minor swelling, certain signs require professional evaluation:
- Fever, severe pain, or redness indicating possible infection.
- Inability to bear weight or sudden loss of mobility.
- Persistent swelling beyond two weeks.
- Sudden, severe swelling after injury suggesting fracture or ligament tear.
Early diagnosis and treatment prevent complications and promote faster recovery.[8]
Prevention Tips
Preventing knee swelling involves adopting healthy habits and protecting the joint:
- Maintain proper posture and ergonomic practices.
- Warm up before exercise to prepare muscles and joints.
- Wear supportive footwear to absorb impact.
- Avoid repetitive stress and high-impact activities that strain the knee.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercises to strengthen surrounding muscles.
- Follow an anti-inflammatory diet and maintain hydration.[9]
Conclusion
Swollen knees are common but can often be effectively managed at home through a combination of rest, ice therapy, gentle exercises, herbal remedies, and dietary adjustments. Early intervention reduces discomfort, promotes faster recovery, and prevents chronic problems. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, strengthening muscles, and avoiding high-impact activities are essential for long-term joint health. Persistent pain, sudden swelling, or signs of infection should prompt medical consultation. By combining home remedies with preventive strategies, individuals can minimize inflammation, maintain mobility, and enjoy a better quality of life.
Helpful strategies at home:
- Apply ice for 15–20 minutes multiple times daily during the first 48 hours
- Elevate the knee while resting
- Gentle massage with anti-inflammatory oils
- Consume a diet rich in omega-3s, calcium, and vitamin D
Check out the related article here:
- Effective Neck Pain Relief Exercises
- Chronic Back Pain Due to Compressed Nerves
- Car Seat Cushions That Reduce Long Drive Fatigue and Back Pain
- Car Backrest Support for Chronic Back Pain Relief
- Posture Fatigue: Why Your Back Hurts After Just 30 Minutes of Sitting
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the best home remedies for a swollen knee?
Rest, ice therapy, gentle massage, herbal remedies like turmeric or ginger, dietary support, and proper elevation.
2. Should I use ice or heat for knee swelling?
Ice is recommended for the first 24–48 hours; heat can be used afterward to relieve stiffness and improve flexibility.
3. How long does knee swelling usually last with home treatment?
Minor swelling typically improves within a few days to a week. Persistent swelling requires medical evaluation.
4. Can exercise help reduce knee swelling?
Yes, gentle strengthening and mobility exercises improve circulation, reduce stiffness, and support recovery.
5. When should I see a doctor for a swollen knee?
Seek medical care if there is fever, severe pain, inability to bear weight, persistent swelling beyond two weeks, or sudden swelling after injury.
References:
- Arthritis Foundation. (n.d.). Osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Foundation. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/more-about/osteoarthritis-of-the-knee Arthritis Foundation
- Healthline. (2024, February 6). 8 home remedies to reduce knee swelling quickly. Healthline. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-reduce-swelling-in-knee-quickly Healthline
- Mayo Clinic. (2022, June 16). Swollen knee – Symptoms & causes. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/swollen-knee/symptoms-causes/syc-20378129 Mayo Clinic
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Knee pain – Diagnosis & treatment (lifestyle and home remedies). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350855 Mayo Clinic
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Knee pain – Symptom: When to see a doctor. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/knee-pain/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050688 Mayo Clinic
- Medical News Today. (n.d.). Swollen knee: Causes, treatments, and home remedies. Medical News Today. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/swollen-knee Medical News Today
- WebMD. (2025?). Knee pain: Overview and home treatment. WebMD. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee-pain/knee-pain-overview WebMD
- Wikipedia contributors. (2025, August). Knee effusion. In Wikipedia. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knee_effusion Wikipedia
- Wikipedia contributors. (2025, August). Osteoarthritis. In Wikipedia. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoarthritis Wikipedia
- Verywell Health. (2021, January 29). 9 at-home treatments for arthritis knee pain. Verywell Health. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/arthritis-knee-pain-treatment-at-home-5100961 Verywell Health
- Verywell Health. (n.d.). How to wrap your knee. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/how-to-wrap-your-knee-5112816 Verywell Health
- Verywell Health. (n.d.). Benefits of knee massage. Retrieved September 3, 2025, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/knee-massage-5092495 Verywell Health