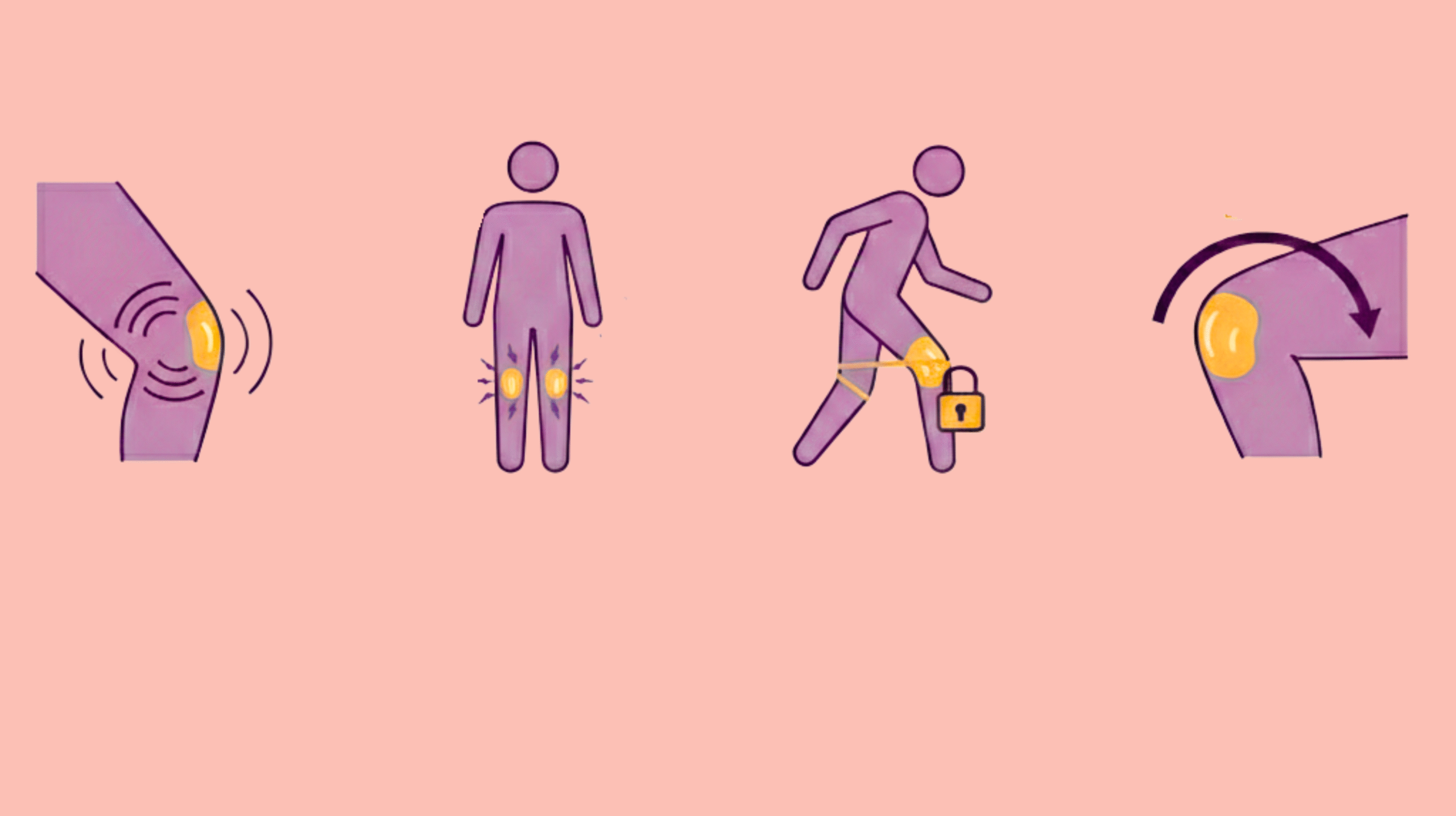
When the knee hurts, you cannot jog in the morning, and you cannot climb stairs or even get out of the couch comfortably. Most of us choose to either disregard or downplay the pain because we think it might be because of getting older or it can be just a strain. There are, however, numerous causes of knee pains and you may leave them unnoticed, but they can turn such little issues in your life into a huge one. With the right knowledge of the causes of knee pain and their treatment, it is essential to maintain your mobility and quality of life.
This article discusses the type of knee pains that the majority of people do not take seriously, their impacts on your day-to-day life, some tips and treatment methods, and activities you can perform at home.
Common Knee Pain Reasons Often Ignored
Osteoarthritis and Degenerative Joint Disease
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common cause of knee pain. Multiple factors can be responsible for this, like age, lifestyle, and previous injuries. Some of the symptoms include pain, stiffness (particularly in the morning or after prolonged sitting), and low mobility. Imagine the knee cartilage to be a shock absorber. As a result of OA, bones get rubbed against one another and lead to wear and tear [1]. The swelling and pain of the body make it difficult to walk, bend and climb up and down steps. Without OA treatment, mobility and quality of life can have a significant impact.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner’s Knee)
No, you don’t have to be a runner to get this one; it’s more common than your daily coffee fix. Runner’s knee occurs when the kneecap isn’t tracking properly and decides to throw a tantrum. Pain usually lurks around or behind the kneecap and worsens with activities such as walking downhill, squatting, or, yes, climbing stairs.
This culprit affects daily life because it turns otherwise normal movements into moments of “Ouch, why did I sit down again?” and “Do the stairs really have to be here?”
Meniscal Tears
Your knee has a cushion of cartilage called the meniscus that is used to stabilize the joint. Aging, sudden twisting, or sports mishaps can be the cause of tears. Knee may become locked or motionless with a tear in the meniscus [2]. Also, you may experience stiffness, pain, and swelling. Meniscal tears are neglected due to the possibility that the pains can resolve themselves in the short term. But they may cause aggravation of the joint damage and difficulty walking without proper treatment.
Ligament Injuries (ACL, MCL)
The strong strips that hold the bones of your knee together are called ligaments. Pain and swelling, as well as weakness, may be experienced in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury. They happen to athletes a lot but also happen due to falls and swift twisting of the knees [3]. When you disregard the damage to ligaments, you put yourself at the risk of falling because your knee becomes weak and unstable. You can also increase the rate of joint damage if you don’t treat the pain.
Bursitis and Inflammation Around the Knee
Bursae are tiny fluid sacs cushioning your knee, but when they get inflamed (bursitis), it’s like the airbag went off for no reason; swelling and tenderness make your knee a hot, painful mess. Daily life impact includes trouble kneeling, bending, or sitting with the knee bent because the swelling feels like carrying a small watermelon right where it hurts the most.
Tendonitis and Overuse Injuries
Tendons connect muscles to bones and can get irritated with repeated activities, leading to tendonitis [4]. Common places include the patellar and quadriceps tendons.
If you’re wondering why your knees flare up after your “just one more set” of squats, now you know. It’s that tendon yelling, “Enough already!” and making daily movements a test of endurance.
How Does Ignoring Knee Pain Affect Daily Life?
Mobility Limitations and Reduced Quality of Life
Ignoring knee pain does not only mean bearing a bit of discomfort but it also means how the pain will influence your daily routine. Stairs are a negotiation with your knees; bending down to tie your shoelaces is like an Olympics activity; stepping to your local coffee shop seems to be a race. In case you are not able to move around that much, you may lack freedom, decrease social engagement, and increase irritation.
Risk of Further Joint Damage and Chronic Pain
If your knees hurt, consider it as a warning sign. Such negligence may cause joint damage, which only increases with time, especially if you have chronic inflammation and sustained pain. Not only is this harmful to your joints, but it also increases the chances of long-term disability and causes additional stress on other joints as your body struggles to compensate.
Psychological and Emotional Effects
The untreated knee pain can be psychologically exhausting. Persistent pain is associated with anxiety, depression and difficulty sleeping [5]. It is a typical example of pain in the body, as well as pain in the mind, because the physical constraints and the psychological outcomes can deteriorate your mood.
Early Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
- Persistent swelling and stiffness that sticks around longer than your favorite TV show binge.
- Sharp or shooting pain during movement that could make you believe you’ve suddenly become accident-prone.
- Knee locking or instability that turns walking into a surprise adventure with unexpected stops.
- Decreased range of motion turning bending your knee into a circus act.
If your knee is playing these tricks, it’s time to pay attention and not just blame it on “getting old.”
Diagnosis and When to See a Doctor
Your doctor will run the knee through its paces; checking swelling, tenderness, stability, and range of motion. Imaging like X-rays or MRI scans might be necessary to see what’s going on underneath. Don’t wait for the knee to start demanding gourmet massages before getting checked; early diagnosis makes treatment simpler and more effective.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): The classic knee care quartet, perfect after acute injuries to calm down inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening the muscles supporting your knee helps stabilize and reduce pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter painkillers like NSAIDs can take the edge off, but don’t become best friends with them without talking to your doctor.
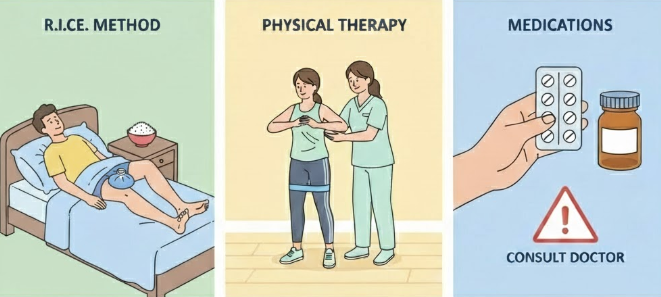
Supportive Devices and Aids
Knee braces and sleeves can offer support and reduce strain; like a gentle hug for your knee. Knee caps help if your patella is out of alignment, guiding it back to its glory days.
Surgical Interventions (When Necessary)
If all else fails and structural damage is severe, surgery such as arthroscopy or knee replacement might be your ticket to getting back in the game. But remember, this is the last resort after trying other options.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies to Manage Knee Pain
Quadriceps and hamstring muscles, which enclose the knee, can be strengthened to reduce the pain and maintain the stability of the joint. Performing knee pain exercises will make your knees feel better by keeping your weight in control. Also, include anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3-rich fish, leafy greens, and nuts to keep the joint inflammation down [6].
Perform low-load exercises such as cycling or swimming to get better health outcomes. Pain relief creams, warm compresses and soft massages can be used at home to relieve pain and enhance circulation.
Preventing Knee Pain in Daily Life
Good posture and ergonomics protect your knees from unnecessary strain. Before your workout, stretch, but don’t go overboard or you’ll have a whole new set of problems. Also, invest in good footwear; a bad shoe is like wearing a thorn in your sole. Proper support can be a real game-changer for your knees.
Conclusion
You do not even credit your knees with the daily adventures you are going through in life. It is just like not listening to a smoke alarm, ignoring why your knee is paining, eventually something will ignite. Once you discover the pain in your knee at the first stage, find appropriate treatment and change your lifestyle, you can significantly improve your mobility and quality of life. Whatever your knees say, listen.
Knee pain often radiates to the bottom, causing ankle or foot pain. Learn effective methods to prevent them as well:
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the most common causes of knee pain that people ignore?
Osteoarthritis, runner’s knee, meniscal tears, ligament injuries, bursitis, and tendonitis top the list.
2. How can knee pain affect daily activities?
It can limit walking, climbing stairs, bending, and even standing for long periods, seriously affecting your lifestyle.
3. When should I see a doctor for knee pain?
If pain is persistent, severe, causing swelling, instability, locking, or impacting daily routine, consulting a healthcare provider is advised.
4. Are knee braces effective in managing knee pain?
Yes, when used appropriately, they support the knee and relieve pain but should be part of a broader treatment plan.
5. What home remedies can help relieve knee pain?
Rest, ice, gentle exercises, weight management, topical creams, and a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help.
References
- Gardner, D. L. (1983). The nature and causes of osteoarthrosis. British medical journal (Clinical research ed.), 286(6363), 418. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.418
- Pasiński, M., Zabrzyńska, M., Adamczyk, M., Sokołowski, M., Głos, T., Ziejka, M., … & Zabrzyński, J. (2023). A current insight into human knee menisci. Translational Research in Anatomy, 32, 100259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tria.2023.100259
- Wheaton, M., & Jensen, N. (2010). The ligament injury is connected to osteoarthritis. Journal of Prolotherapy, 2(1), 294-304. https://www.prolotherapy.com/pdf-general-articles/GA-014-The-ligament-injury-connection-to-osteoarthritis-(2011).pdf
- Ashton-Miller, J. A. (1999). Response of muscle and tendon to injury and overuse. In Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders: Report, Workshop Summary, and Workshop Papers, National Research Council (pp. 73-97). https://europepmc.org/books/n/nap6431/ddd00061/?extid=25101461&src=med&fid=ddd00062
- Li, G. Z., Ji, R. J., Xu, C. P., Yang, L. J., & Moreira, P. (2025). On Patient Quality of Life: Impacts of Knee Osteoarthritis on Pain, Anxiety, Depression, Fatigue and Sleep Disorders. Nursing Open, 12(7), e70264. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.70264
- Black, J. K. (2012). More Anti-Inflammation Diet Tips and Recipes: Protect Yourself from Heart Disease, Arthritis, Diabetes, Allergies, Fatigue and Pain. Turner Publishing Company. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=In_uEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT15&dq