Shoulder pain is a common issue that many people experience, especially as they get older. One of the most common causes of chronic shoulder pain is rotator cuff tendinopathy. The rotator cuff plays a crucial role in stabilizing your shoulder joint, and when it becomes damaged or irritated, it can lead to ongoing pain and stiffness. In this blog, we will explore what rotator cuff tendinopathy is, what causes it, and how it can manifest into other conditions.
What is Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy?
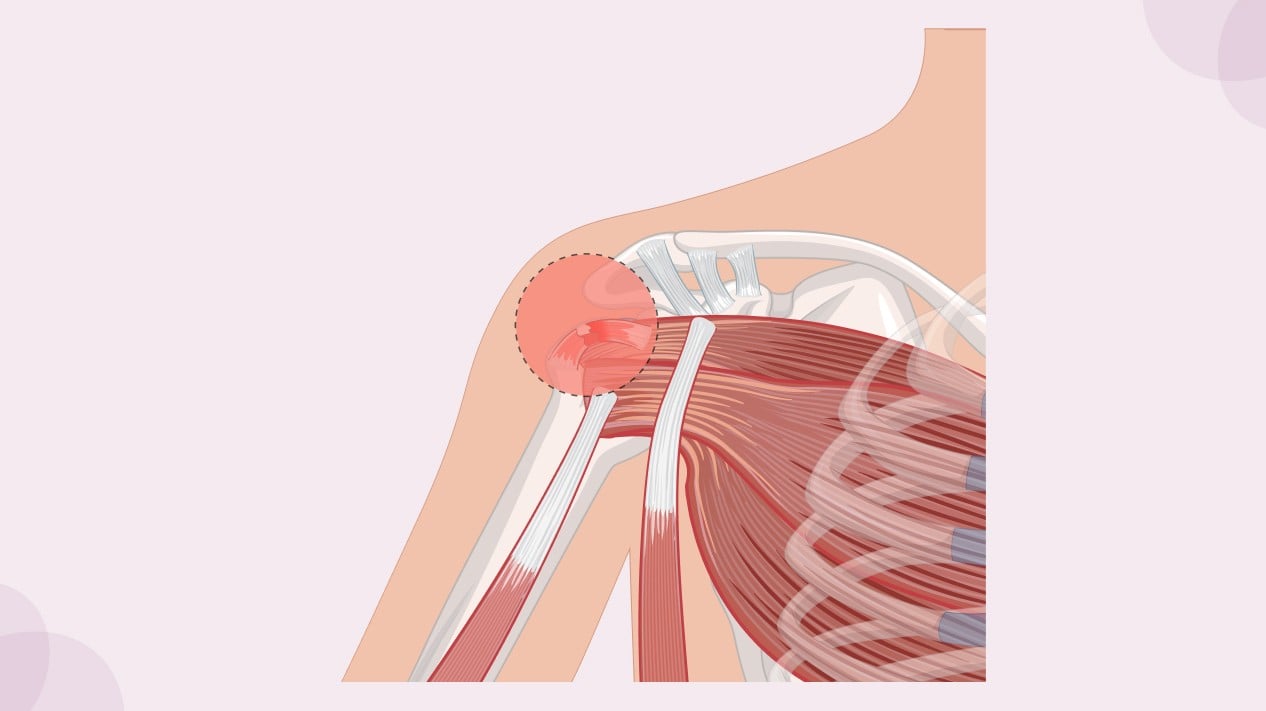
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that surround the shoulder joint. These muscles are responsible for stabilizing the shoulder and enabling its wide range of motion. When the tendons of the rotator cuff are subjected to repetitive stress, they can become irritated, inflamed, or even tear, leading to rotator cuff tendinopathy.
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is essentially an overuse injury. It is characterized by damage or degeneration of the tendons, leading to pain, stiffness, and a decrease in the shoulder’s mobility. People with this condition may experience difficulty raising their arm, reaching behind their back, or performing everyday tasks like lifting grocery bags or combing their hair.
What Causes Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy?
Rotator cuff tendinopathy often results from repeated stress or strain on the shoulder joint. This can occur due to several factors, including:
- Repetitive Movements: Activities that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as swimming, tennis, or weightlifting, can put constant strain on the rotator cuff tendons, leading to wear and tear over time.
- Poor Posture: Poor posture, particularly slumping or hunching forward, can affect the alignment of the shoulder joint and place extra stress on the rotator cuff muscles. Over time, this strain can lead to tendinopathy.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weakness in certain shoulder muscles, especially those around the shoulder blade, can lead to imbalances that affect the way the rotator cuff functions. This can cause uneven forces on the tendons, making them more prone to injury.
- Aging: As we age, the tendons in the rotator cuff naturally lose their elasticity and strength. This can make them more vulnerable to damage, even with normal movements.
- Trauma or Injury: A sudden injury, like a fall or direct blow to the shoulder, can also contribute to rotator cuff tendinopathy. This is especially true if the injury involves excessive force or overstretching of the tendons.
What Health Conditions Does Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Lead To?
If left untreated, rotator cuff tendinopathy can lead to a number of other issues that affect the shoulder joint. These include:
- Muscle Wear and Tear: As the tendons in the rotator cuff continue to deteriorate, the muscles that support them may also begin to weaken and wear out. This can further reduce the strength and stability of the shoulder, making it difficult to perform tasks that require lifting or reaching.
- Muscle Imbalance: Over time, imbalances between the different muscles around the shoulder can develop. For example, if the rotator cuff muscles weaken, the larger shoulder muscles, such as the deltoid, may take on more of the workload, leading to further strain and imbalance.
- Tendon Tears: In more severe cases, rotator cuff tendinopathy can lead to partial or full tears of the tendons. A tear can significantly impair the function of the shoulder and often requires surgical intervention for repair.
- Frozen Shoulder: Chronic shoulder pain caused by rotator cuff tendinopathy can lead to stiffness and restricted movement, sometimes resulting in frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis). This condition causes significant pain and a marked reduction in the range of motion of the shoulder joint.
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: The inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons can cause them to become compressed or pinched between the bones of the shoulder, leading to shoulder impingement syndrome. This condition causes pain, particularly when raising the arm overhead, and can further aggravate tendinopathy.
How Do You Know if Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy is the Cause of Your Shoulder Pain?
The symptoms of rotator cuff tendinopathy can vary, but some of the most common signs include:
- Pain and tenderness in the front or top of the shoulder
- Pain that worsens with overhead movements or lifting
- Stiffness or limited range of motion in the shoulder
- A feeling of weakness in the arm, especially when lifting or reaching
- Pain that worsens at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider who can diagnose the condition. Your doctor will perform a physical examination and may use imaging techniques such as X-rays or MRI scans to assess the damage to the tendons and muscles.
How is Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Treated?
Fortunately, there are several effective treatments for rotator cuff tendinopathy. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, promote healing of the tendons, and restore strength and mobility to the shoulder. Some common treatments include:
- Rest and Ice: Giving your shoulder time to rest and applying ice can help reduce inflammation and pain. Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is essential for healing.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can help you strengthen the muscles around the shoulder, improve your posture, and restore the shoulder’s range of motion. This can help relieve stress on the rotator cuff tendons and prevent future injuries.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area.
- Steroid Injections: For severe pain, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and provide relief.
- Surgery: In cases where the tendons are severely damaged or torn, surgery may be necessary to repair the tendons and restore shoulder function. This is typically considered a last resort after other treatments have failed.
Conclusion: Preventing and Managing Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a common cause of chronic shoulder pain, especially for those who engage in repetitive overhead motions or suffer from muscle imbalances. The good news is that with early intervention, most people can manage the condition effectively without the need for surgery. If you’re experiencing chronic shoulder pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider who can help diagnose the condition and guide you through a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
By addressing factors like posture, muscle imbalances, and repetitive stress, you can reduce your risk of developing rotator cuff tendinopathy and improve your shoulder health for the long term.
References
- Koo, J. H., & Lee, S. M. (2018). Rotator cuff tendinopathy: Pathophysiology and management. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 27(9), 1567-1575. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29902260/
2. Hsu, J. E., & Gupta, R. (2020). Rotator cuff tendon disorders. Orthopedic Clinics of North America, 51(4), 539-548. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33066368/
3. Nho, S. J., & Yocum, L. A. (2019). Muscular imbalances and rotator cuff tendinopathy. Sports Medicine Journal, 47(3), 381-388. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30702076/
4. Zhang, X. Z., & Li, H. (2019). Repetitive shoulder movements and rotator cuff injuries. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 14(1), 46. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30821202/
5. Zhang, Y., & Wang, Z. (2020). Physical therapy interventions for rotator cuff tendinopathy. Journal of Rehabilitation Research, 59(5), 394-402. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33108547/